In this article following topics will be covered;
-
Full form of computer
-
Definition of computer
-
What is a computer
-
Block diagram of a computer
-
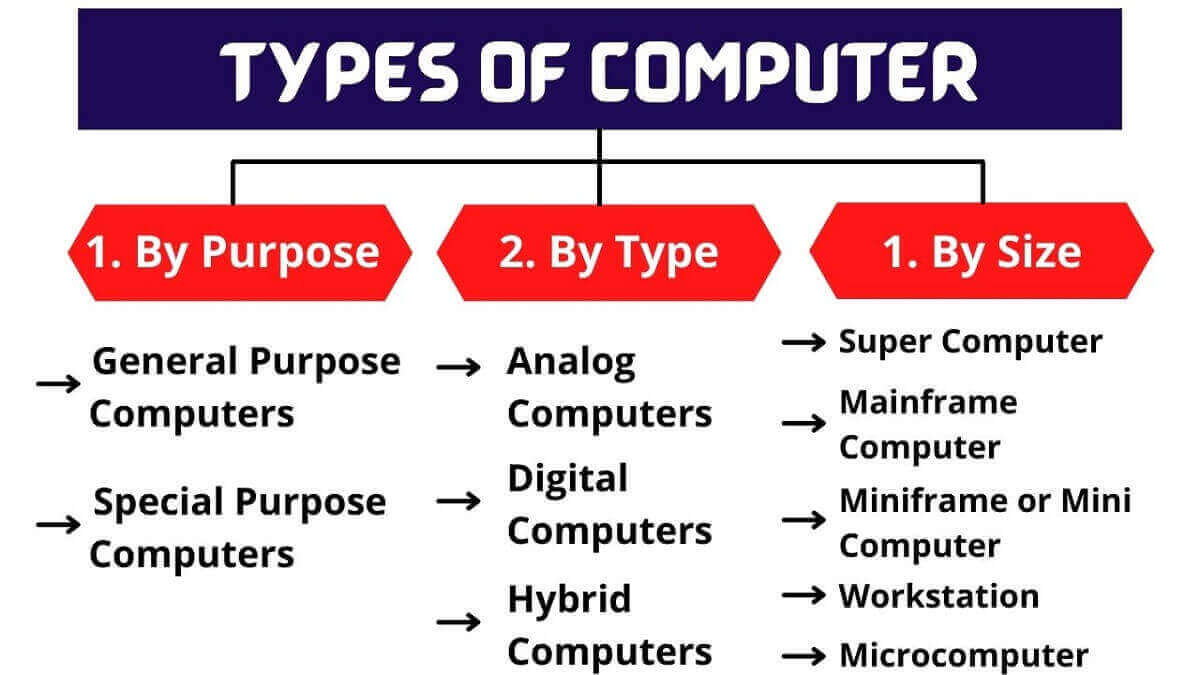
Types of computer
-
Difference between hardware and software
-
Full form of computer-related terms like URL full form, ups full form, CPU full form. and ram full form etc.
Full form of computer:
You might have heard the Fullform of computer is “Common Operating Machine Purposely used for Technological and Educational Research”. However, it is not true.
The word computer is not a short form or an acronym rather, it has been derived from the word “compute” which means to calculate. Initially, a computer was designed to do simple calculations hence this name was derived. But now the use of computers is not limited to calculations only rather all the important tasks associated with human life have been assigned to the computers.
Definition of Computer:
A computer is an electronic device that uses raw information as data and processes it accordingly to give the required result. The main function of the computer is to store, retrieve, and process data. Now a day’s its uses have been extended to type documents, play online games, web browsing, editing & creating spreadsheets, office presentations, PowerPoint meetings & video consoles, etc.
What is a Computer?
In early history, computers were basically used for numerical calculations. In any case, as any information can be numerically encoded, people after a short time comprehended that PCs are good for comprehensively valuable information taking care of. Their capacity to manage a ton of data has extended the reliability data of environment assurance. Their speed has allowed them to make decisions about guiding telephone relationships through an association and to control mechanical structures like vehicles, nuclear reactors, and robotized cautious devices. No doubt to say in this 5th generation scenario the perfect use of AI (artificial Intelligence) really invokes the world for many drastic changes. Sofia-A Hunson Robotics manufactured shows the perfect example of AI.

Sophia was named in the United Nations Development Programme‘s (UNDP) first-ever Innovation Champion and the first non-human to be given any United Nation title.
Block diagram of a computer:
The block diagram of a computer is shown in the below figure;
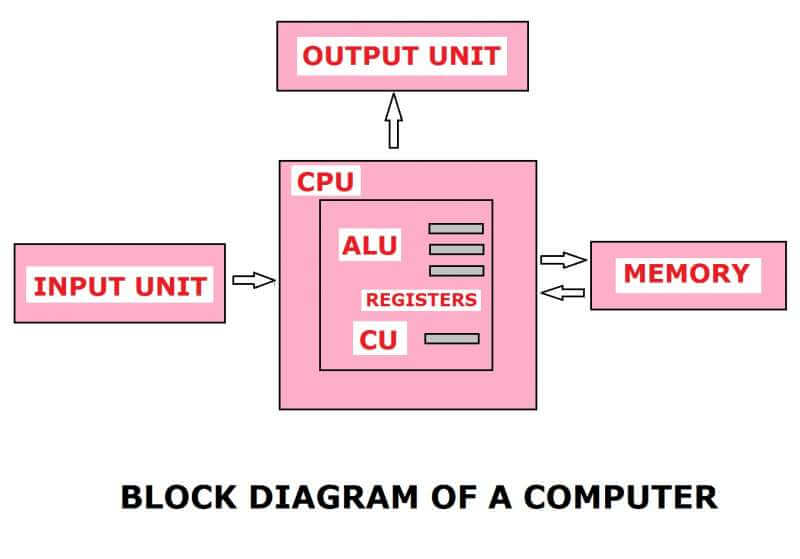
A computer basically contains the following units;
1. Input Unit: A input unit is used for feeding the data to the computer. For example Keyboard, mouse, joystick and scanner, etc.
2. CPU: Full form of CPU is the Central processing unit and it is considered as the heart of a computer. All data processing is done in the CPU itself.
3. ALU: ALU stands for Arithmetic Logic Unit. It is contained inside the CPU. All mathematical calculations are done in the ALU
4. Memory: It is a very important unit. All data is stored in the memory itself. The memory can be temporary or permanent.
5. Output Unit: The processed data is delivered through the output unit. The computer screen and printer is an example of the output unit.
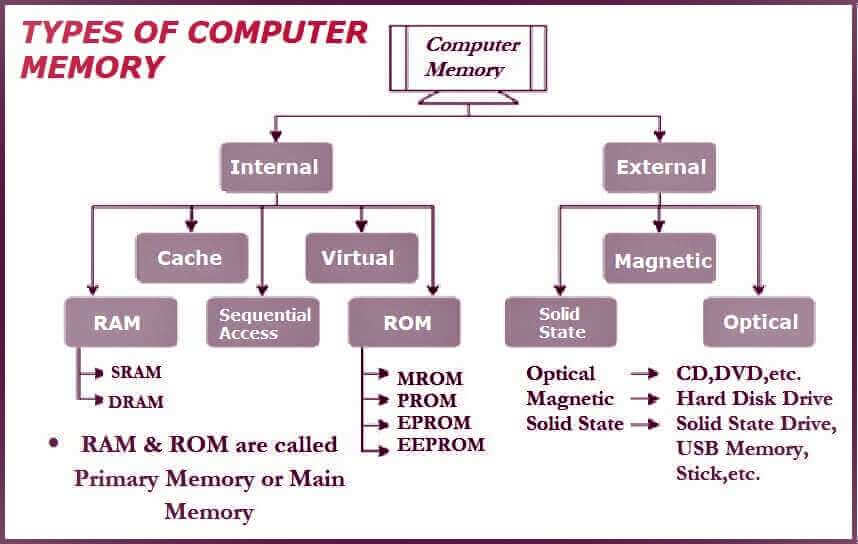
Types of computer memory:
Types of computer memory are explained in the below figure;
Types of computers:

People generally think of a general-purpose computer when the word COMPUTER is said, but it can be primarily a desktop or laptop. The computer comes in different shapes and sizes, and they perform many different functions in our daily lives.
DESKTOP COMPUTERS:
As the name suggests most of the people use PCs at work, home, and school. Desktop computers are proposed to be put on a work region merely on the table and they comprise two or three different parts, including the PC case, screen, control center along with mouse.
LAPTOP & TABLET COMPUTERS:
The Laptop & Tablet Computers are battery-filled PCs that are more helpful than desktop computers, allowing one to use them almost anywhere. Tablet handheld PCs that are impressively smaller than PCs. These days iPad’s set the most suitable example of tablets that are most handy & comfortable.
SERVERS:
A “local server”, localhost are various names associated with this computer that serves information to other computers on a wide network area. For example, whenever we use the Internet, a server is a repository for web pages that responds when someone requests a certain website. This ‘request’ is simply the act of entering the web address into a browser and hitting return something that’s stored on a server. Some businesses also use local file servers to store and share files internally.
In the client/server programming model, a host program expects and fulfills requests from client programs, which might be running on something comparative or various PCs.
Other types of computers:
Some of today’s electronics are basically specialized computers, though we don’t always think of them that way. The most common examples are:
Smartphones: Cell phones work merely what computers can do, including browsing the Internet and playing games, such gadgets are often called smartphones. This technology can also be used in devices—including fitness, smartwatches, advanced oximeter, that are designed to make life comfortable.
- Game consoles: For playing video games on TV, a specialized type of computer with proper adjustment with computer is required.
- Advanced & Automatic TVs: Many TVs allow you to access various types of online content including various OTT platforms. Netflix, Zee 5, Amazon Prime, etc. really changed the world of Television. Nowadays films are also released on these types of OTT platforms, allowing the users to watch the first day first show.
Difference between hardware and software:
(HARDWARE VS. SOFTWARE);
The most common thing that comes to the mind of the users is hardware and software.
- Hardware is the part of the computer that has a physical touch, such as the keyboard or mouse. It also includes all of the computer’s internal parts, which can be seen after the opening of the CPU.
- Software is any set of instructions that instructs the hardware what to do and how to do it. Examples include web browsers, games, and word processors, MS word, Powerpoint, MS Accord, etc.
Everything you do on your computer will rely on both hardware and software. For example, right now you may be viewing this lesson in a web browser (software) and using your mouse (hardware) to click from page to page. As you learn about different types of computers, ask yourself about the differences in their hardware. As you progress through this tutorial, you’ll see that different types of computers also often use different types of software.
MAKE YOUR WEB BROWSER MORE EFFECTIVE OR THE EFFECTIVE WAYS TO MAKE YOUR PC FAST
Getting the information easily & more clearly is the need of the hour today. Following are the tips & tricks to make your browser fast;
- Bookmarks: Most visited sites can be linked with bookmarks. This facility allows one to quickly find information that one has come upon before.
- Tabbed Browsing: Tabbed Browsing allows the user to have opened up multiple windows at a single time. Opening multiple windows make the work faster & convenient too. But be careful! If you have too many open, it can slow the performance.
- Homepage: The homepage also provides you with quick access to the web. Most people use sites like Google, Yahoo!, MSN, and Hotmail which provide both options of search tools along with news and entertainment.
- Stop Button: Stop button or the ads Blocker, often pages with ads take a long time to load or stop the other websites to open, In these cases, the stop button can be really helpful. If you want the web page that didn’t load you need an ads blocker or the stop button, to stop reload the page and wipe it out.
- Search Engine: Google, Bing, Yahoo! These search engines came by default when you open a window. You should change this setting to the search engine that you prefer better for use.
Full form of computer-related terms:
| TERMS | FULL FORMS |
| URL | Uniform Resource Locator |
| CPU | Central Processing Unit. |
| UPS | Uninterruptible power supply or Uninterruptible power source |
| RAM | Random Access Memory |
| ROM | Read Only Memory |
| USB | Universal Serial Bus |
| OCR | Optical Character Recognition |
| DVD | Digital Versatile Disc |
| CD | Compact Disc |
| SQL | Structured Query Language |
| NIC | National Informatics Centre |
| VLSI | Very Large-Scale Integration |
| VIRUS | Vital Information Resources Under Siege |
| IPE | Intelligent Peripheral Equipment |
| MAC | Media Access Control Address |
| WAN | Wide Area Network |
| LAN | Local Area Network |
| CMOS | Complementary Metal Oxide Semiconductor |
| ISO | Optical Disc Image |
| VPN | Virtual Private Network |
| MS | Microsoft (Ms) Or Microsoft Corporation |
| FTP | File Transfer Protocol |
| IPS | Intrusion Prevention System |
| RDBMS | Relational Database Management System |
| DBMS | Database Management System |
| PDA | Personal Digital Assistant |
| ENIAC | Electronic Numerical Integrator And Computer |
| DOS | Disk Operating System |
| DDoS | Distributed Denial Of Service |
| MICR | Magnetic Ink Character Recognition |
| CRT | Cathode-Ray Tube |
| GOI | General Operating Instructions |
| HTTP | Hypertext Transfer Protocol |
| HTTPS | Hypertext Transfer Protocol Secure |
| BN | Binary Number |
| HTML | Hypertext Markup Language |
| WWW | World Wide Web |
| WWWW | World Wide Web Worm |
| ALU | Arithmetic Logic Unit |
| IPO | Input–Process–Output |
| ISP | Internet Service Provider |
| BIOS | Basic Input Output System |
| PC | Personal Computer |
| SMPS | Switched-Mode Power Supply |
| Portable Document Format | |
| PCI | Peripheral Component Interconnect |
| ASCII | American Standard Code For Information Interchange |
| IP | Internet Protocol |
| TCP | Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol |
| BASIC | Beginner’s All-Purpose Symbolic Instruction Code |
| COBOL | Common Business-Oriented Language |
| SSD | Solid State Drive |
| DTP | Desktop Publishing |
| LED | Light Emitting Diode |
| OMR | Optical Mark Reading |
| VDU | Visual/Video Display Unit |
| DNS | Domain Name System |
| ICT | Information And Communication Technologies |
| PPP | Point-To-Point Protocol |
| POP | Post Office Protocol |
| OSI | Open Systems Interconnection |
| LCD | Liquid-Crystal Display |
| AI | Artificial Intelligence |
| BPN | Back Propagation Neural Network |
| PNG | Portable Network Graphics |
| JPEG | Joint Photographic Experts Group |
| ATM | Automated Teller Machine |
| SSL | Secure Sockets Layer |
| API | Application Programming Interface |
| WAP | Wireless Application Protocol |
| CU | Control Unit |
| MIPS | Million Instructions Per Second |
| PAN | Personal Area Network |
| OS | Operating System |
| FAT | File Allocation Table |
| PHP | Personal Home Page |
| EBCDIC | Extended Binary Coded Decimal Interchange Code |
| ULSI | Ultra Large Scale Integration |
| GSM | Global System For Mobile Communications |
| CAD | Computer-Aided Design |
| FORTRAN | Formula Translation |
| BCC | Blind Carbon Copy |
| CSS | Cascading Style Sheets |
| HTML | Hypertext Markup Language |
| AI | Artificial Intelligence |
| VGA | Video Graphics Array |
| ERP | Enterprise Resource Planning |
This article is written by;
MR. ABHISHEK SRIVASTAVA
B.TECH (MECHANICAL ENGG.)
- 4+ Years of Industrial Experience
- 2+ Years of Teaching
E-Mail: [email protected]

Recent Comments